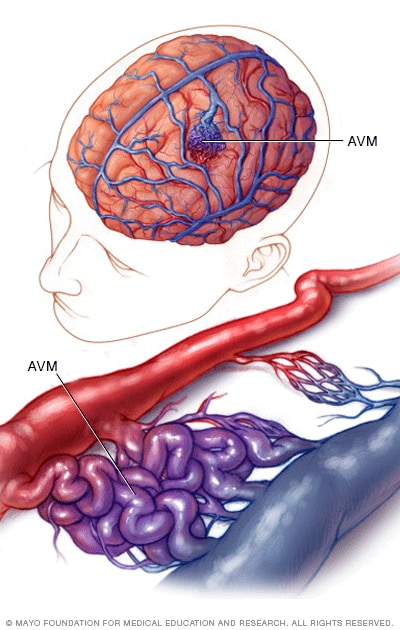
AVM Brain - Arterio-Venous Malformations (of Brain)
An AVM is Arteriovenous Malformation, where there is tangling of the arteries and veins.
The arteries are responsible for carrying out oxygenated blood to various parts of the body from the heart. The Arteries carry blood with high pressure, this is supported by the thick elastic wall present in them which helps to sustain the blood pressure. Whereas veins carry deoxygenated blood back to heart from the body. This is in contrast to the fact that veins don't have to carry blood with pressure, thus the blood flow is sluggish as compared to arterial flow. To support this sluggish blood flow, there are valves present inside veins which prevent backflow of blood.
Thus any intertwining of these two blood vessels is problematic. This can occur anywhere in the body, these are very rare in the brain and occur as a result of developmental abnormality majority of the times.
A Brain AVM may or may not cause any signs and symptoms. But the signs and symptoms arise when there is rupture of AVM which results in the hemorrhage.
Some people may experience signs and symptoms other than bleeding or associated with the after effects of bleeding. It includes
- seizures
- headache or pain in one area of head
- vision loss
- difficulty in speaking
- severe unsteadiness
- Confusion
- Muscle weakness or numbness in one part of the body
Risk factors
Anyone can be born with a brain AVM, but these factors may be a risk:
- Being male. AVMs are more common in males.
- Having a family history. Cases of AVMs in families have been reported, but it's unclear if there's a certain genetic factor or if the cases are only coincidental. It's also possible to inherit other medical conditions that predispose you to having vascular malformations such as AVMs.
- Hemorrhage
- Ischaemia to the tissues surrounding the AVM
- Weak blood vessels
- Brain Damage
- AVM can be treated by surgical technique. Where the AVM is located and then removed surgically.
- AVM can also be treated by Radiational methods, where the Radiation is given to the spot where the AVM lies and thus due to radiation effect, it vanishes down.
- AVM can also be treated by embolectomy procedure, where the AVM is clogged with a fluid which is more viscous and thus prevents the further blood flow to the AVM causing it to reduce in size and resolve.
Contact us - @_uzumakisenpai_ @creativesparkblogs
Author - Dr. Yogiraj Karambelkar



Comments
Post a Comment