CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY - 1
The cell is the basic and most fundamental structure of the human body. It contains all the things required for the functioning.
A cell is basically the command centre. Millions of such command centres gather together to form an organism. The 1st cells to form are the stem cells. They form the basis of the human body. There are various properties of stem cells that include pluripotency, multipotency, nullipotent and totipotency.
This video shows the mitotic division of the stem cell. Note the mitotic spindle formed that leads to division.
As the zygote further grows the fundamental properties of cell become more potent. This is where the cells decide their functions and behave as they are. This property of cell is called as differentiation; a process where the cell takes up a particular function or cells of particular function gather up to perform a function later turning into a tissue and organ. This event generally happens in the 2nd and 3rd week of intrauterine life (or the period of life when you are inside the uterus). 4th week marks the duration of organogenesis. Organogenesis is the process where organs are formed from the differentiated cell clusters. An interesting fact to note here - The 1st heartbeat that ever takes place is in the 4th week and the heart thereafter doesn't stops beating. It just keeps on going till the end of the life.
Neuronal cells are formed and then migrate to organs where the neural tissue is present.
1st neuronal cells derived from stem cells.
This process continues till all the organs and their tissues are formed.
The cell itself is a tiny organ with multiple small organelles that function to keep it in existence. The energy giving "mitochondria" is an example of an organelle that is inside the cell.
FUN FACT: Mitochondria is not only responsible for energy production. It has its own genetic material which is responsible for development of the eyes and vision of the baby. Also, only the head of the sperm fertilises during the process; hence the mitochondria is left out and the ovum acts as the source of mitochondria. Hence all eye related disorders example myopia, are maternally inherited or colour blindness, maternally inherited. It is believed that, organelles like mitochondria were an independent organisms who were able to generate energy, hence they fused up with non energy generating organisms to help aid in survival of both as mitochondria didn't have any specific protection.
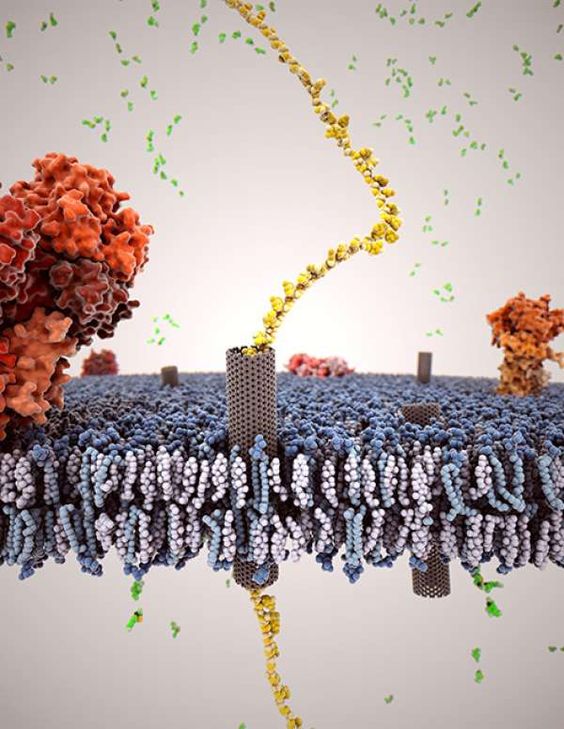
The cell is fluid in nature. Here, fluid doesn't mean it is liquid, but fluid indicates it adapts to the surrounding environment. The cell allows only certain materials to enter and leave. This property of the cell is called as "selectively permeable". This is possible only when there are certain proteins, or channels that allow this to happen. All of these channels are present inside the cell membrane of the cell. The cell membrane is a double layered covering which contains phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, fats, etc.
Cholesterol is an important portion of the cell membrane. It acts as a fluid buffer, i.e. it maintains the fluid nature of the cell membrane.
Proteins inside the cell membrane helps to maintain the structure of the cell.
This image shows the cell membrane.
The cell has certain proteins that help in the function of transport of certain substances.
The 3 main proteins that help in movement inside the cell are - Kinesin, Dynein, Tubulin.
Kinesin helps in signal transfer from the Cell body to synaps
Dynein helps in signal transfer from Synapse to cell body,
This is exactly how the rabies and polio infection takes place. There is increased activity of kinesin and dynein proteins.
Dynein also helps in the function of movement of sperm.
The cells are tightly bound to each other by certain molecules. These molecules are called as junctions.
Zona Occludens (ZO) aka Tight junction. These are rope like connections between cells present on these locations predominantly - Blood brain barrier, Intestines, Kidneys, Choroid plexus. They ensure zero leak of substances into the intercellular matrix.
Adherens junction - Attached to actin (a muscle filament)
Desmosomes - Predominantly seen in heart, uterus and skin. These are present in the intermediate filaments as in keratin, laminin, vimentin, etc.
Gap junction - Located in heart, neurons, smooth muscles. Gap junctions are formed by proteins called as connexons (made of 6 individual units called as connexins). Cardiac gap junctions are present in the intercalated discs.






Comments
Post a Comment