Nerve Injuries
The deformities and injuries that lead to the neuronal damage is called as nerve injury. It can be caused by trauma or can be present by birth. But most commonly, trauma is the leading cause of nerve injuries.
Axillary nerve and musculocutaneous nerve - Root value - C5 and C6
Axillary nerve has a sensitive part and motor part. Sensory part is called as the Regimental Badge area.
Most common cause of axillary nerve injury is shoulder dislocation.
It presents as adduction + internal rotation.
Management is very easy. Using splint that holds the arm in abduction + external rotation position.
Musculocutaneous nerve presents as extension and pronation of the limb. Most commonly caused by the dislocation of shoulder.
Median nerve - Also called as the labourer's nerve. Supplies the flexor component of the forearm including the thenar eminences, lumbricles 1 & 2.
Injury to the median nerve can occur at the following areas -
1. @wrist - wasting of muscles, loss of flexion, abduction, opposition of the hand. This is called as APE HAND deformity with loss of sensation in the areas supplied by it. Pen test is done where palm is facing upwards and the person is asked to touch the pen using the thumb.
2. @elbow - it shows Clasp hand deformity (aka - Oschner clasp hand) + wrist lesions are shown.
Because of loss of action of flexor pollicis longus, flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus, there is loss of flexion of index finger.
On performing Oschner clasp hand test, where patient is asked to clasp hands together, the index finger fails to flex and remains pointing out. This is called as pointing index finger sign or sign of Benediction or benediction sign.
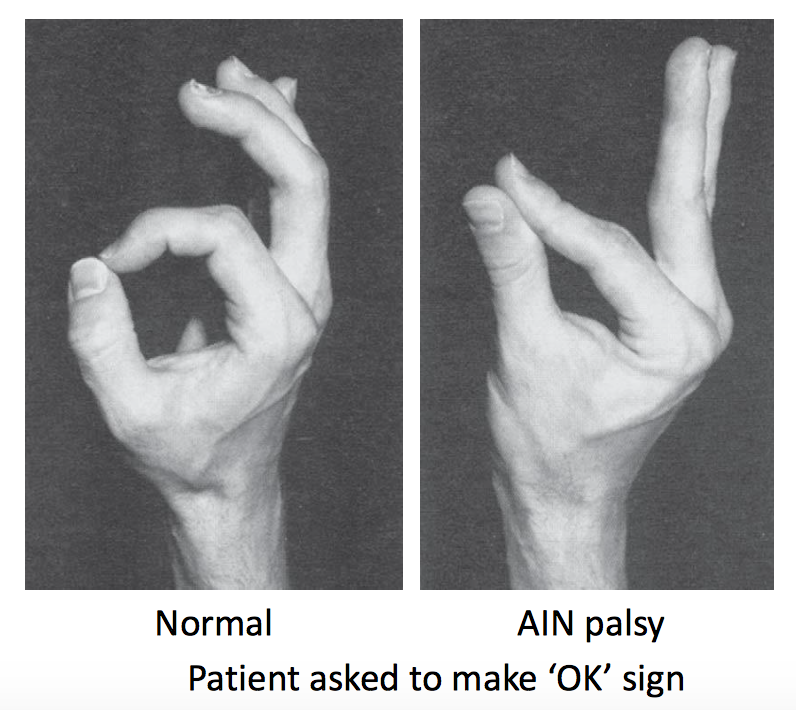
If there is isolated median nerve injury, it affects on the anterior interosseous nerve which is pure motor in action. It happens in Supracondylar fracture of humerus. This results in loss of function of flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitorum profundus. This leads to proper flexing of metacarpophalangeal joints and proximal interphalangeal joints, but not able to flex Distal interphalangeal joint and interphalangeal joint of index and middle finger.
This is tested by performing OK test. The patient is asked to make the OK sign, he/she is not able to do so and thus results in weak OK sign. This is called as Kiloh Nevin sign.
Ulnar nerve - AKA musician's nerve.
Supplies medial and 1/4th of the fingers (sensory) + Predominant supply to the intrinsic muscles of the hand (motor).
1. Injury @medial epicondyle - leads to partial claw hand deformity with altered sensation to the area affected.
complete claw hand deformity is seen when there is median + ulnar nerve injury.
Tests for ulnar nerve injury - Card test (adduction is checked)
Egawa test (tests the abduction, fanning of fingers is a positive test)
Book Test - Hold book between thumb and index finger, if there is Flexion, it indicates weakness, this is called as Froment sign.
Radial Nerve Injury - Most commonly injured nerve.
Caused by Holstein-Lewis fracture (lower 1/3rd fracture of humerus)
Palsy of radial nerve leads to -
1. Low injury - finger + thumb drop + loss of sensation.
2. High injury - wrist drop + loss of sensation
3. Very High injury - triceps function is lost, leading to flexion of elbow.
Easy way to remember is, if the lesion is distal to Extensor carpi radialis longus - NO WRIST DROP
if the lesion is proximal to Extensor carpi radialis longus - WRIST DROP.
This can be treated by splinting. It the lesion is early 2 types of splints can be used -
1. Static cock-up Splint
2. Dynamic cock-up Splint.
If the presentation is Late - Tendon transplant is done and no benefit is seen from splinting.
Wrist drop - pronator teres tendon is used
Finger drop - flexor carpi ulnaris tendon is used
Thumb drop - flexor carpi radialis tendon is used





Comments
Post a Comment